Next-Gen AI-Powered Cybersecurity
for a Safer Digital Future
Protecting businesses, governments, and infrastructure with
autonomous,
intelligent, and adaptive security solutions.
- Instant Threat Detection. Automated Response.
- Deploy in minutes — no complex setup
- Managed Detection and Response (MDR)
- Cloud-Native
Built on a Zero-Compromise Security Foundation
Comprehensive Security Monitoring
Detect threats across endpoints, networks, and cloud environments with centralized monitoring.
Real-Time Threat Detection
Leverage real-time analytics and correlation to identify suspicious activity quickly.
Automated Incident Response
Respond faster with built-in automation that helps contain threats and reduce manual work.
Seamless Integrations
Works smoothly with popular tools like Elastic Stack, SIEMs, and cloud providers.
Unified Visibility and Reporting
Get complete insights through dashboards and customizable compliance reports.
Alert Prioritization
Cut through noise with prioritized alerts focused on real risks.
Sentinel Security Metrics
Real-time operational overview of defensive posture.
Since last system restart
Currently authenticated users
Patched and fully compliant
Global response time (ms)
Simple Pricing Plans for Maximum Security
Choose the layer of protection that fits your organization, from free tools to full MDR.
Free Essentials
- Next-gen malware defense
- Firewall management
- Device control
- IT hygiene
- Identity protection
- Log Retaintion 7 Days
- Unleash the power of ML
- Threat intelligence & hunting
Sharabha GO
- All Free features, PLUS
- Endpoint detection and response (EDR)
- Log Retaintion 15 Days
- Unleash the power of ML
- Threat intelligence & hunting
- Next-gen SIEM
- Wavro Chat Assistance Limited Access
- MDR (Managed Detection and Response)
Sharabha PRO
- All Go features, PLUS
- Threat intelligence & hunting
- Next-gen SIEM
- Wavro Chat Assistance Full Access
- MDR (Managed Detection and Response)
- Log Retaintion 30 Days
- Dedicated Express support
- Priority security patches
For Enterprise Solutions:
Custom XDR, 24/7 MDR, and unlimited data retention tailored for large organizations.
Contact Sales for Custom PricingWe Specialize In XDR Excellence
Empower your business with intelligent, automated cyber defense—maximize security, minimize complexity, and stay ahead of modern threats.
Attack Surface Coverage
Monitor endpoints, network, cloud, and identity from one unified dashboard.
AI Threat Hunting
Use machine learning and behavioral analytics to find hidden threats early.
Automated Remediation
Auto-block and contain threats with smart, rapid, and evolving responses.
Rapid Forensics
Quickly trace attacks and find root causes with advanced investigative tools.
Trusted by Leaders in Every Sector
Protecting diverse organizations globally with XDR.
Magnified Digital
Crop Sync
LBSATI
Uniqoor
Taaffeife Infratech
RNKS
Identify More Threats Instantly with AI
Endpoints remain the primary targets for cyberattacks, yet 84% of breaches involve multiple attack vectors. Octopyder XDR® unifies data across endpoints, cloud environments, networks, and identity systems—leveraging artificial intelligence to detect, correlate, and prioritize threats regardless of their origin.

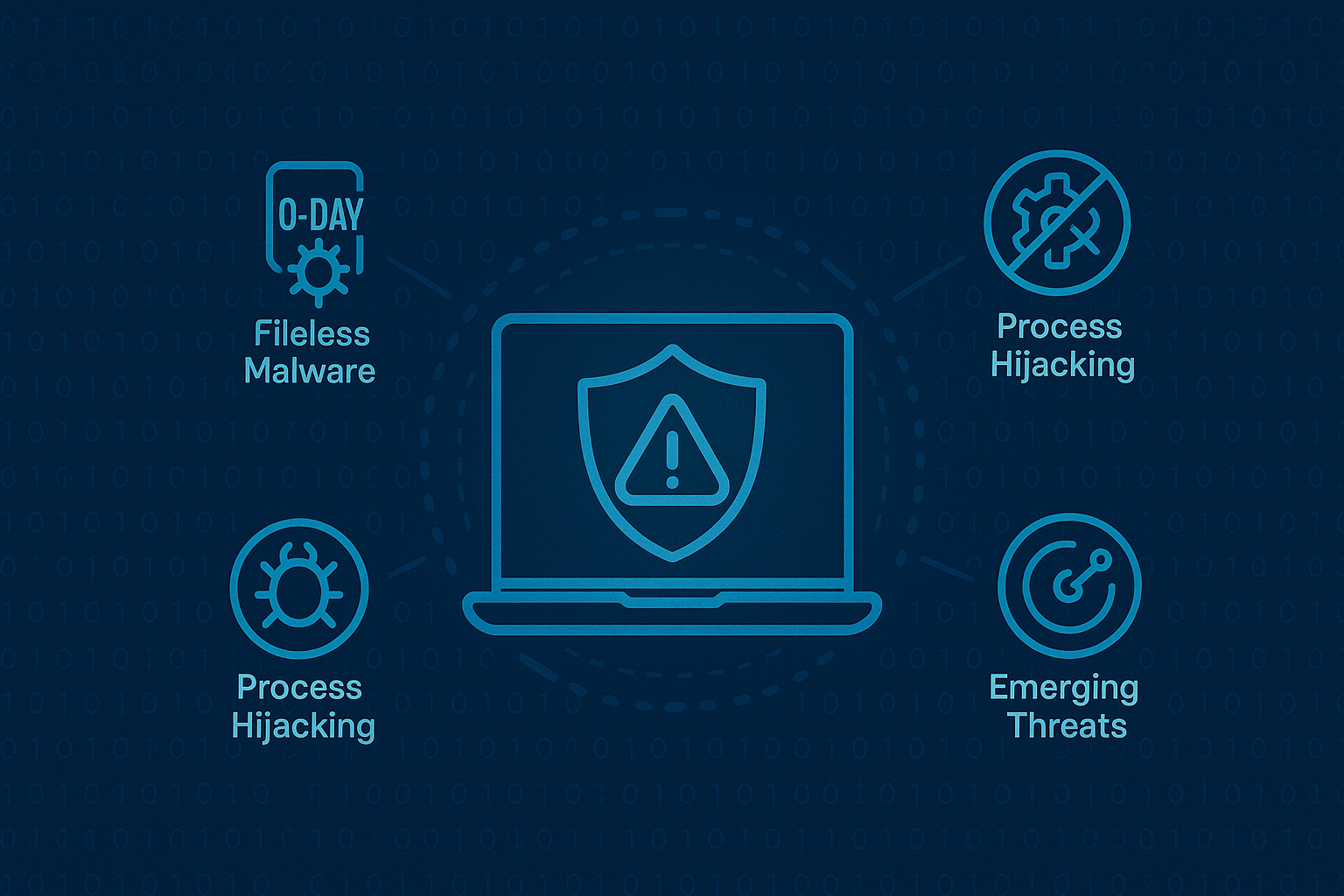
Stop Endpoint Threats with Unmatched Precision
Cyber adversaries use countless tactics to breach your endpoints — and preparation is key. That’s why Octopyder XDR® integrates advanced prevention modules designed to counter every modern attack method, from zero-day exploits and fileless malware to process hijacking and emerging threats yet to appear.
Uncover Root Causes and Reduce Investigation Time to Minutes
When attackers gain a foothold, every second matters. You might detect indicators of compromise or malicious files—but understanding how they appeared is crucial. Octopyder XDR® reveals the full execution trail behind each alert and uses built-in automation to break the entire attack chain in minutes, not hours or days.
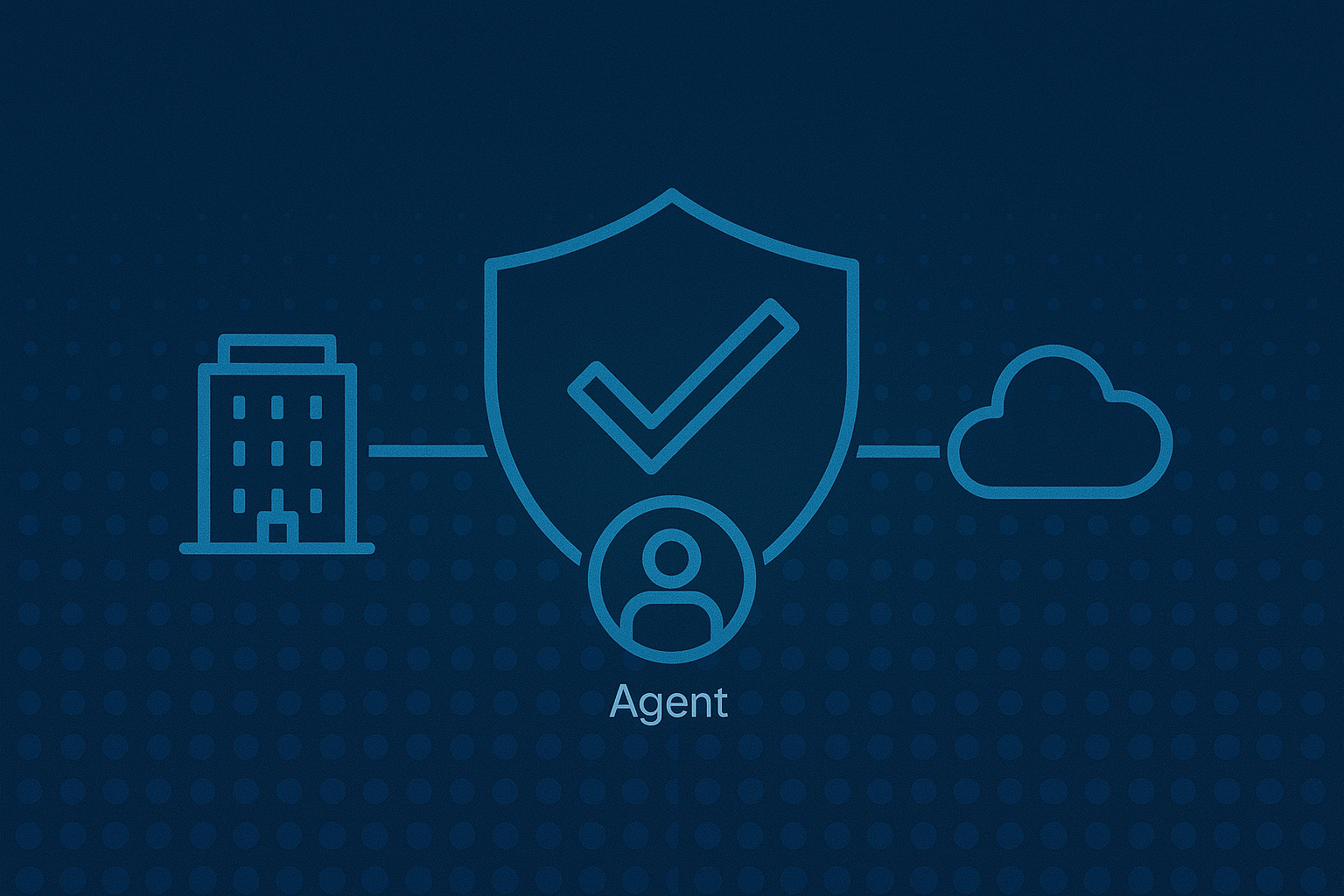
Defend Against Sophisticated Attacks with a Single Agent for Enterprise and Cloud
While cloud environments operate differently, your security standards shouldn’t have to change. The unified Octopyder XDR® agent provides industry-leading cloud detection and response (CDR), ensuring real-time protection across every layer of your multicloud infrastructure.

Elevate Your SOC with an AI-Powered Platform Beyond XDR
Take XDR to the next level with the Octopyder Platform, combining advanced NG-SIEM, SOAR, ASM, and cloud security features into a single, seamless ecosystem. Enjoy a unified backend, intuitive interface, and streamlined analyst experience—all designed to transform how your SOC operates.

Meet Our Cyber Vigilance Team
The brilliant minds and dedicated experts behind the XDR platform, ensuring 24/7 security and threat intelligence.

HIMANSHU HARSH
CEO, Ethical Hacker

AJEET KUMAR
COO, Data Engineer

NISHANT KUMAR
Cyber Secruity (VAPT)

RANA JYOTI
Engineer, ML Developer

VIPIN SAINI
Engineer, ML Developer

PRIYANSHU KUMAR
Web Developer
Stop Breaches. Start XDR. Seamlessly.
Unify your security across endpoints, network, and cloud. Detect, investigate, and eliminate threats faster with true Extended Detection and Response.
No credit card required. Explore our capabilities.
Testimonials
“Ready to see what our clients are saying? Read what they’re saying about Octopyder’s innovative threat detection solutions and discover how we’re protecting businesses from today’s most sophisticated cyber threats!”



